How to Read the Periodic Table Ppt
How is the periodic table of the elements arranged?
Arrangement of elements in the Periodic Table
Effigy shows the Periodic Table in use today.
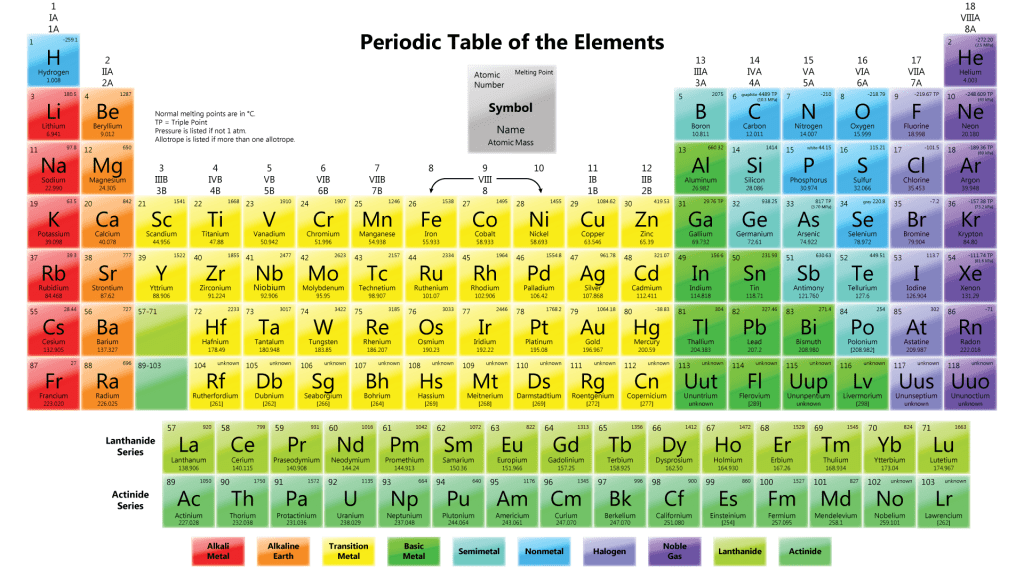
Elements are arranged horizontally Inascending order of theirproton numbers, from 1 to 116, in the Periodic Table.
Groups
- Definition:Eachvertical column of elements in the Periodic Table is known as agroup.
- Elements with thesame number of valence electrons are bundled in thesame group.
- There are18 vertical columns of elements in the Periodic Table known as Grouping i, Group 2, until Group 18.
- Group 1 elements are known equallyalkali metals.
- Group iielements are known asalkaline globe metals.
- Group three to Group 12 elements are known every bittransition elements.
- Group 17 elements are known every bithalogens.
- Grouping 18 elements are known asnoble gases.
Periods
- Definition: Eachhorizontal row of elements in the Periodic Tabular array is known as amenstruation.
- There areseven horizontal rows of elements in the Periodic Table, known as Menstruation 1, Period 2, until Period 7.
- Periods ane to 3 areshort periods while Periods iv to 7 arelong periods.
- Period 1 contains 2 elements.
- Periods 2 and iii incorporate eight elements respectively.
- Periods iv and 5 contain 18 elements respectively.
- Menstruum 6 contains 32 elements.
- Catamenia vii contains 27 elements.
- Although Period six contains 32 elements, elements with proton numbers 57 to 71 are arranged separately at the bottom of the Periodic Table. This series of elements is calledlanthanides.
- Similarly, elements with proton numbers 89 to 103 in Flow 7 are arranged separately at the bottom of the Periodic Table. This serial of elements is chosenactinides.
Metal and non-metal properties
- Element inGrouping 1, 2 and13 aremetals.
- Transition elements inGrouping 3 to12 are alsometals.
- Elements inGroup 15, 16, 17 and18 arenon-metals.
- In Grouping 14,
- Carbon and silicon arenot-metals.
- Germanium is ametalloid (semimetal)
- Tin and atomic number 82 aremetals.
1. Relationship betwixt the electron arrangement and the position of the chemical element in the Periodic Tabular array
Figure shows the electron arrangements of the elements with proton numbers 1 to 20 in the Periodic Table.

2. Relationship between the electron arrangement and the group number of an chemical element
- Based on above Effigy, thegroup number of an chemical element is determined bythe number of valence electronsin an cantlet of the element.
- Table shows the relationship between the number of valence electrons and the group number of an element.

- For elements with 1 or ii valence electrons,
Group number of that element = Number of valence electrons - For elements with 3 to viii valence electrons,
Group number of that element = Number of valence electrons plus x
Note:
Helium with an electron arrangement of 2 is placed in Group 18. This is an exception.
This is because helium has similar inert backdrop as the other noble gases in Group eighteen.
Example:Element Q has a nucleon number of 27. An atom of element Q contains 14 neutrons. In which group is element Q located in the Periodic Tabular array?
Solution:
Number of electrons in an cantlet Q = Number of protons
= 27 – fourteen = xiii
Electron arrangement of atom Q = 2.8.3
Number of valence electrons = 3
∴ Group number = 3 + 10 = xiii
Hence, element Q is located in Group thirteen of the Periodic Table.
3. Relationship betwixt the electron arrangement and the flow number of an element
- Based on above Figure, the flow number of an element is determined by the number of shells occupied with electrons in an atom of that element.
- Table shows the relationship between the number of shells occupied with electrons and the period number of an element.

- Hence,
Period number of an chemical element = Number of shells occupied with electrons in an atom of that element
Instance:Element T has a proton number of 19 and a nucleon number of 39. In which catamenia is element T located in the Periodic Tabular array?
Solution:
Number of electrons in atom T
= Number of protons in atom T
= Proton number =19
∴ Electron organization of cantlet T = 2.8.viii.i
Atom T has iv shells occupied with electrons. Hence, chemical element T is located in Menstruum 4 of the Periodic Table.
Instance:Element R is located in Grouping 15 and Period 3 of the Periodic Table. What is the electron system of an atom of chemical element R?
Solution:
Atom R has 5 valence electrons because it is in Group 15.
Atom R has 3 shells occupied with electrons because information technology is in Flow 3.
Electron system of atom R = 2.8.5
4. Elements with thesame number of valence electronswill exhibitsimilar chemical properties.
For example:
Atom W with an electron arrangement of two.8.2 and atom X with an electron arrangement of 2.8.8.2 exhibitsimilar chemical properties.
This is because both the atoms of West and Tentake 2 valence electrons, that is thesame number of valence electrons.
Periodic Table Mnemonics
Mnemonics are like shooting fish in a barrel-to-remember lines or phrases one can use to memorize things that are hard to learn. In this article, you lot will notice Hindi mnemonics – one each for one grouping – to learn the Periodic Table
The Periodic Tabular array provides the names, diminutive numbers, symbols and atomic weights of known elements. It serves as a great tool for solving chemistry bug.
A periodic table is divided into groups (columns), where elements with each grouping behave similarly while bonding with other elements; and periods (rows), where elements in i period have same number of electron shells.
Here are some fun, interesting and naughty mnemonics in Hindi used by the backbenchers to memorize elements along each grouping or period:
Cardinal To Reading These Mnemonics Or Hindi Sentence:
• These sentences contain letters denoting symbols of elements in the same order as they occur in a group or menstruation.
• The symbols have been highlighted as bold letters in the sentence. However at the places where the complete symbol could not be included in the sentence, the first letters have been strung together and the 2d alphabetic character is shown in brackets. While reading the sentence you don't take to read the messages in bracket. Merely keep them in mind.
• At some places, phonetics accept been used to denote a symbols such every bit 'c' could be replaced by 'grand','one thousand' with 'j', 'I' with 'ea' and 'o' with 'u', to make the sentence easier to remember.
S-Block Elements
Consisting of the outset two groups, S-block elements accept quite similar concrete and chemic properties. The valence electrons of the elements in this block occupy south-orbitals.
Group one is known as alkali metals. It includes Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (Yard), Rubidium (Ru), Caesium (Cs), and Francium (Fr).
Mnemonic for Group 1:LiNa KiRupastCseFriendship hai.
Group 2 is known as element of group i earth metals. It includes Beryllium (Be), Magnesium (Mg), Calcium (Ca), Strontium (Sr), Barium (Br), and Radium (Ra).
Mnemonic for Group ii:BetaMangeCarSouthwardcooterBaaprane seRaazi
P-Cake Elements
Consisting of last half-dozen groups of the periodic tabular array (Groups 13 to 18), P-cake elements have their valence electrons occupying p-orbitals. This block consists of not-metals, semi-metals and poor metals.
Group 13 is known every bit Boron group or the group of Icosagens or Triels. It includes Boron (B), Aluminium (Al), Gallium (Ga), Indium (In), and Thallium (Tl).
Mnemonic for Group xiii:B A G I T.
Grouping 14 is known equally Carbon grouping or the group of Crystallogens, Tetragens or Tetrels. Information technology includes Carbon (C), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Tin (Sn), and Atomic number 82 (Lead).
Mnemonic for Grouping 14:ChemistrySirG4due eastsSouthwardankiProblems.
Group 15 is known as the grouping of Pnictogens or Nitrogen group. Information technology includes Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), and Bismuth (Bi).
Mnemonic for Grouping 15:NorthwardahiPasandAiseSabBhai.
Group 16 is known as the grouping of Chalcogens or Oxygen group. It includes Oxygen (O), Sulphur (S), Selenium (Se), Tellurium (Te), and the radioactive chemical element Polonium (Po).
Mnemonic for Grouping 16:Oh!StyleSeTelPolish.
Group 17 is known as the group of Halogens. Information technology includes Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), and Astatine (At).
Mnemonic for Grouping 17:FirCall karBahaar AayIAunited nationsty.
Group xviii is known every bit the group of Noble gases, excluding Helium. Ordinarily, they are all odorless and colorless gases with very low chemical reactivity. The grouping includes Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe), and the radioactive Radon (Rn).
Mnemonic for Group xviii:HeNeverArrived;YardaraXeroRun pe out.
D-Cake Elements
D-Block elements consist of element groups 3 to 12 that correspond to the filling of the d-orbital subshell of the second outermost shell. Groups 3 to eleven are besides known as transitional metals. Group 12 elements, which have its d subshell completely filled, are besides known equally mail-transition elements.
D-block elements and F-block elements prove considerable similarities beyond the periods too.
Nosotros can memorize these elements across the periods:
Period iv elements are quite stable and many of them are very common in earth's chaff or cadre or both. D-cake elements it includes are Scandium (Sc), Titanium (Ti), Vanadium (5), Chromium (Cr), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), Nickel (Ni), Copper (Cu) and Zinc (Zn).
Mnemonic for Period 4:ScienceTi(ea)cherVineetaCriplani1000an Fenko (FeCo)Ni Kyun(Cu)Zaadue north hai?
Read as: Scientific discipline Instructor Vineeta Kriplani manfenko ni kyun zaan hai?
Period 5 elements are known to fill their 5s beat beginning, then 4d shells and then 5p shells, with rhodium being the exception. The elements of this period show many exceptions to Maledung dominion. D-block elements it includes are Yttrium (Y), Zirconium (Zr), Niobium (Nb), Molybdenum (Mo), Technetium (Tc), Ruthenium (Ru), Rhodium (Rh), Pd (Palladium), Silver (Ag) and Cadmium (Cd).
Mnemonic for Period v:YehZarraNabi banaMohabaat meinT(c)eri, R(u)o R(h)oP(d)ukarogiAaj(g) iseChandni
Read as: Yeh Zarra Nabi bana Mohabbat mein Teri, Ro Ro Pukarogi Aaj ise Chandni
Menses half-dozen includes the lanthanides or rare earths. Some of these transition metals are very valuable such as gold. D-block elements it includes are Lutetium (Lu), Hafnium (Hf), Tantalum (Ta), Tungsten (Westward), Rhenium (Re), Osmium (Bone), Iridium (Ir), Platinum (Pt), Aureate (Au) and Mercury (Hg).
Mnemonic for Period six:Fifty(u)aHafTaWestwardarnaRehUs(Os)IrritatingPopat ke saathAurHoj(g)a pagal.
Read as: La Hafta Warna Reh U.s. Irritating Popat ke saath Aur Hoja pagal.
Period 7 contains the radioactive elements but. It includes actinides which include the heaviest naturally occurring element Californium. All other elements are synthesized artificially. D-block elements
information technology includes are Actinium (Ac), Rutherfordium (Rf), Dubnium (Db), Seaborgium (Sg), Bohrium (Bh), Hassium (Hs), Meitnerium (Mt), and Darmstadtium (Ds).
Mnemonic for Period 7:Ak(c)eleR(f) D(b)S(thousand)harma kiB(h)ook meinH(s)ainMaths keDifficultsawaal.
Read as: Akele R D Sharma ki Volume mein Hain Maths ke Hard sawaal.
F-Block Elements
F-block elements have their valence electrons in f-orbitals. They are also known as inner transition elements. They tin be divided into Lanthanides (too known as rare world elements) and Actinides that are highly reactive to halogens and chalcogens similar lanthanides but they react more hands.
Lanthanides include Cerium (Ce), Praseodymium (Pr), Neodymium (Nd), Promethium (Pm), Samarium (Sm), Europium (Eu), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysprosium (Dy), Holmium (Ho), Erbium (Er), Thulium (Tm), Ytterbium (Yb) and Lutetium (Lu).
We tin can learn all these in three parts:
- Cerium (Ce), Praseodymium (Pr), Neodymium (Nd), Promethium (Pm), and Samarium (Sm)
Mnemonic for Lanthanides Part 1:Celina aurPrietyNeastdande sePammy aurSimmy ko mara.
- Europium (European union), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysprosium (Dy), and Holmium (Ho)
Mnemonic for Lanthanides Office 2:EuropeM(d)aya toTB(b) aurDi(y)arrohoeaHo gaya.
Read as: Europe Gaya to TB aur Diarrohoea Ho gaya.
- Erbium (Er), Thulium (Tm), Ytterbium (Yb) and Lutetium (Lu)
Mnemonic for Lanthanides Office iii:East rdue east, dekhTamatarYellow aurbLue hain.
Actinides include these f-block elements – Thorium (Th), Protactinium (Pa), Uranium (U), Neptunium (Np), Plutonium (Pu), Americium (Am), Curium (Cm), Berkelium (Bk), Fermium (Fm), Mendelevium (Md), Nobelium (No), and Lawrencium (Lr).
We can learn all these in three parts too:
1. Thorium (Thursday), Protactinium (Pa), Uranium (U), and Neptunium (Np)
Mnemonic for Actinides Role 1:ThodePehelwanUnseNiptengey.
two. Plutonium (Pu), Americium (Am), Curium (Cm), Berkelium (Bk)
Mnemonic for Actinides Part ii:PuraneAamThou(C)amBikenge.
Read as: Purane Aam Kam Bikenge.
- Fermium (Fm), Mendelevium (Physician), Nobelium (No), and Lawrencium (Lr)
Mnemonic for Actinides Part 3: ItniFayardily aMdani meinNoFiftyadkirajee.
Source: https://www.learncbse.in/how-to-learn-periodic-table/
0 Response to "How to Read the Periodic Table Ppt"
Post a Comment